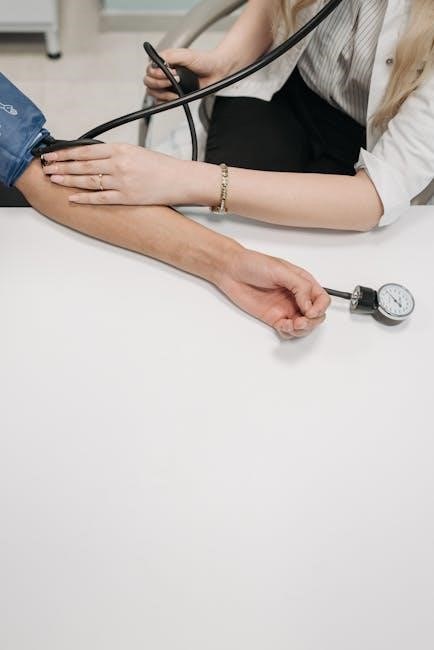
A manual blood pressure cuff is a device used to measure blood pressure, requiring a stethoscope to listen to heart sounds․ It is essential for accurate readings and proper technique to ensure reliable results, making it a vital tool for both medical professionals and home use․ Regular use helps monitor heart health effectively, providing consistent and precise data for better health management․
1․1 What Is a Manual Blood Pressure Cuff?
A manual blood pressure cuff is a non-digital device used to measure blood pressure, requiring a stethoscope to detect heart sounds․ It consists of an inflatable cuff, a valve, and a pressure gauge․ This tool is widely used in clinical and home settings due to its simplicity and reliability․ Unlike automatic monitors, manual cuffs rely on user technique, making proper training essential for accurate readings․ They remain a preferred choice for their cost-effectiveness and accuracy when used correctly․
1․2 Importance of Accurate Blood Pressure Measurement
Accurate blood pressure measurement is crucial for diagnosing and managing hypertension․ Inaccurate readings can lead to misdiagnosis, improper treatment plans, and poor health outcomes․ Proper technique and reliable equipment ensure precise data, which is essential for monitoring heart health and making informed decisions․ Consistent and correct measurements help track changes over time, enabling effective management of blood pressure and reducing cardiovascular risks;

Key Features of a Good Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
A good manual blood pressure cuff should have proper cuff size, durable materials, and easy-to-use features․ It must include a reliable inflation system and a clear pressure gauge for accurate readings․ Additionally, a high-quality stethoscope with both bell and diaphragm capacity is essential for clear heart sound detection, ensuring precise blood pressure measurement․
2․1 Cuff Size and Fit
Cuff size and fit are crucial for accurate blood pressure measurements․ A cuff that is too small or too large can lead to incorrect readings․ The American Heart Association recommends that the cuff’s bladder length should be at least 80% of the arm circumference, and its width should be at least 40%; Proper fit ensures comfort and precision, making it essential to choose a cuff that suits the user’s arm size․ Incorrect sizing can result in inaccurate readings, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right cuff for reliable results․
2․2 Durability and Build Quality
A good manual blood pressure cuff should be made from durable materials, such as high-quality nylon or latex, ensuring longevity․ Sturdy stitching and metal components, like the inflating bulb and valve, enhance its reliability․ A well-constructed cuff withstands frequent use and maintains accuracy over time; Durable designs often include replaceable parts, extending the product’s lifespan․ Proper build quality ensures consistent performance, making it a dependable tool for both professional and home use․
2․3 Ease of Use
Ease of use is crucial for accurate blood pressure measurement․ A good manual cuff should come with clear instructions and an intuitive design, making it simple for users to inflate the cuff and listen to heart sounds with a stethoscope․ Features like one-touch measurement and easy-to-read guidelines can enhance the user experience, ensuring consistent and precise readings without unnecessary complexity, all while maintaining reliability․
How Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs Work
A manual blood pressure cuff measures blood pressure by inflating to restrict blood flow, then deflating while using a stethoscope to detect heart sounds, providing systolic and diastolic readings․
3․1 The Role of the Stethoscope
The stethoscope is a crucial tool for manual blood pressure measurement, allowing healthcare professionals to detect heart sounds․ It features both a bell and diaphragm, providing clarity for systolic and diastolic pressures․ Proper placement on the brachial artery ensures accurate readings․ The stethoscope’s sensitivity is vital for capturing clear sounds, making it an indispensable component of the manual blood pressure cuff system․ Its use requires skill and attention to detail for reliable results․
3․2 The Process of Measuring Blood Pressure
To measure blood pressure manually, place the cuff around the upper arm, ensuring proper fit․ Inflate the cuff to restrict blood flow, then gradually deflate it while listening to artery sounds through a stethoscope․ Systolic pressure is heard as the first sound, and diastolic as the sounds fade․ Accurate results depend on correct cuff placement, steady deflation, and careful listening․ Proper technique is essential for reliable readings․
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Proper cuff placement and environment significantly impact accuracy․ Ensuring the cuff is correctly positioned and avoiding external noise helps achieve precise readings․ Technique consistency is crucial for reliable results․
4․1 Proper Cuff Placement
Proper cuff placement is critical for accurate blood pressure measurements․ The cuff should be wrapped snugly around the upper arm, positioned at heart level, and centered directly above the elbow crease․ Ensuring the cuff is neither too tight nor too loose is essential to avoid errors․ Incorrect placement can lead to inaccurate readings, emphasizing the importance of following guidelines to achieve reliable blood pressure readings․ Proper technique guarantees precise and consistent results․
4․2 Environment and Technique
The environment and technique significantly impact the accuracy of blood pressure readings․ A quiet, comfortable setting is essential to avoid distractions․ Proper positioning, such as sitting upright with the cuff at heart level, ensures reliable results․ Incorrect techniques, like moving or talking during measurement, can lead to inaccurate readings․ Following guidelines, such as avoiding caffeine and ensuring the cuff is properly inflated, is crucial for precise data․ Consistency in method helps maintain reliability․
Choosing the Right Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
Selecting the right manual blood pressure cuff involves considering factors like cuff size, durability, and ease of use; Various types are available, catering to different needs, ensuring accuracy and comfort․ Prioritize brand reputation and user reviews to make an informed decision․
5․1 Types of Cuffs Available
Manual blood pressure cuffs come in various styles to suit different needs․ The most common are upper arm cuffs, recommended by the AHA/AMA for accuracy․ Wrist cuffs are portable but less precise․ Pediatric and large adult sizes ensure proper fit for diverse users․ Reusable cuffs are durable, while single-use options are ideal for clinical settings to prevent cross-contamination․ Each type offers unique benefits, catering to individual preferences and requirements for accurate blood pressure measurement․
5․2 Brand and Reviews
When selecting a good manual blood pressure cuff, considering the brand and reviews is essential․ Reputable brands often adhere to medical standards, ensuring accuracy and durability․ Reading reviews can provide insights into user experiences, highlighting features like ease of use and consistency․ Look for endorsements from healthcare professionals or organizations, as they often recommend trusted models․ A well-reviewed manual blood pressure cuff is more likely to deliver reliable results, making it a worthwhile investment for monitoring heart health effectively․

Maintenance and Care
Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is essential․ Store in a dry place to prevent damage․ Inspect cuffs and valves regularly for signs of wear and tear․
6․1 Cleaning and Storage
Regular cleaning and proper storage are crucial for maintaining the accuracy and longevity of a manual blood pressure cuff․ Use a soft, damp cloth with mild soap to wipe the cuff and bladder, avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive materials․ Allow it to air dry completely before storing․ Keep the cuff in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight, and ensure it is rolled or folded neatly to prevent creases or damage․ Regular inspection for signs of wear and tear is also essential․
6․2 Regular Inspection
Regular inspection of a manual blood pressure cuff is crucial to ensure accuracy and longevity․ Check the cuff for cracks, frays, or worn-out material, and verify the stethoscope’s proper function․ Ensure all connections are secure and free from damage․ Inspect the inflation bulb, valve, and gauge for leaks or malfunctions․ Replace any damaged parts promptly to maintain reliable performance․ Proper storage and cleaning also contribute to the cuff’s durability and accuracy over time․
Advantages Over Automatic Monitors
Manual blood pressure cuffs are cost-effective, portable, and reliable, requiring no batteries, making them ideal for home use and medical settings without relying on electronic components․
7․1 Cost-Effectiveness
A good manual blood pressure cuff is a cost-effective option for monitoring blood pressure․ It requires a one-time purchase and no ongoing expenses, making it more affordable than automatic monitors․ Without the need for batteries, manual cuffs are both economical and environmentally friendly․ Their durability ensures long-term use, providing great value for money․ This makes them an excellent choice for both home and professional settings, offering accurate readings without additional costs․
7․2 Portability
A good manual blood pressure cuff is lightweight and compact, making it easy to carry in a bag or suitcase․ Its design eliminates the need for batteries, ensuring reliability in any setting; This portability is ideal for travel or clinical use, allowing users to monitor blood pressure anywhere without worrying about power sources․ The convenience of manual cuffs enhances their practicality for everyday health monitoring․
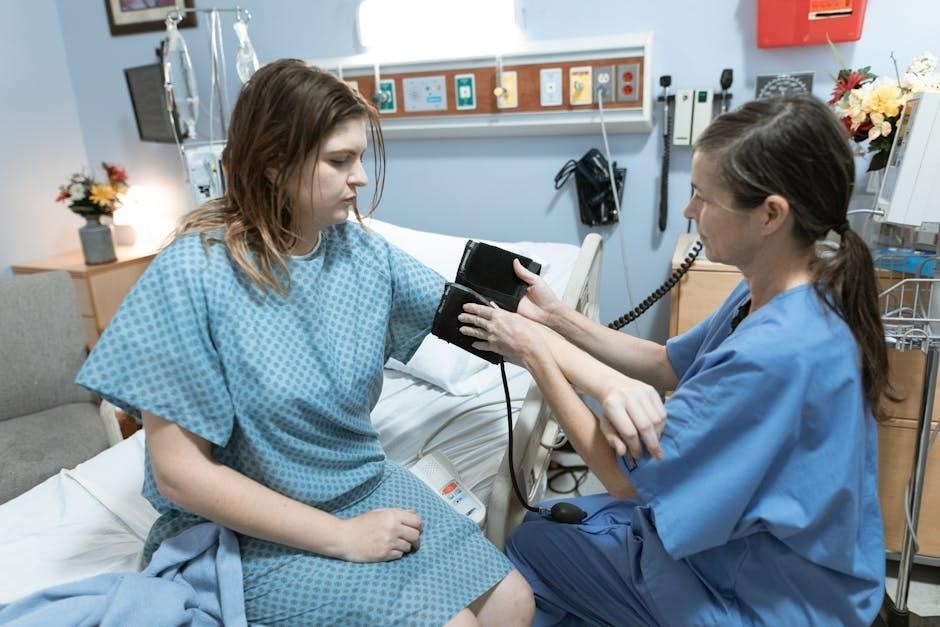

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Using an incorrect cuff size and improper technique are common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate readings․ Ensure the cuff fits properly and follow guidelines carefully․
8․1 Incorrect Cuff Size
Using a cuff that is too small or too large can lead to inaccurate blood pressure readings․ A cuff that is too small may overestimate pressure, while one that is too large may underestimate it․ Proper sizing is crucial for reliability․ Ensure the cuff fits the upper arm correctly, with the lower edge about 1 inch above the elbow․ Always follow sizing guidelines to avoid errors and ensure precise measurements for better health monitoring and decision-making․ Correct cuff size is essential for accurate results․
8․2 Improper Technique
Improper technique is a common issue when using a manual blood pressure cuff․ Incorrect placement, failure to inflate the cuff adequately, or rushing the deflation process can lead to inaccurate readings․ Additionally, not using the stethoscope correctly or misinterpreting heart sounds can affect results․ It is crucial to follow proper guidelines and receive training to avoid these errors, ensuring reliable and accurate blood pressure measurements every time․
A good manual blood pressure cuff is a reliable tool for accurate readings, ensuring proper health monitoring․ Regular use and correct technique are essential for consistent results, making it a valuable investment for long-term health management․
9․1 Summary of Key Points
A good manual blood pressure cuff ensures accurate readings when used correctly․ Proper cuff size, technique, and stethoscope use are crucial for reliability․ Regular maintenance and avoiding common mistakes, like incorrect cuff placement, enhance accuracy․ Manual cuffs are cost-effective, portable, and ideal for both professional and home use, providing consistent heart health monitoring․ Adhering to guidelines and proper care ensures long-term functionality and precise blood pressure measurement․
9․2 Final Recommendations
When selecting a manual blood pressure cuff, prioritize proper fit, durability, and ease of use․ Always follow guidelines for cuff size and technique to ensure accuracy․ Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection, is crucial for longevity․ Avoid common mistakes like incorrect cuff placement and improper stethoscope use․ Investing in a high-quality cuff and stethoscope with both bell and diaphragm capacity will yield reliable results․ Consistent practice and adherence to best practices will enhance your ability to obtain accurate readings․
